QUES . How would a decline in Total Fertility Rate (TFR) below the replacement level, in many states of India affect the future population structure of the country?
HINTS:
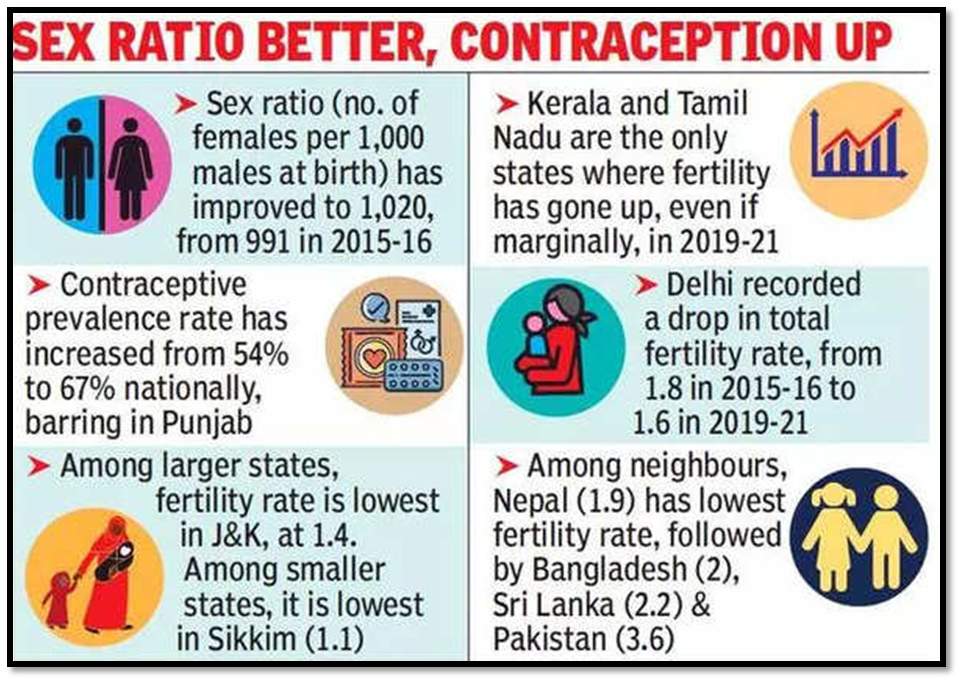
TFR of about 2.1 children per woman is called Replacement-level fertility. TFR lower than 2.1 children per woman — indicates that a generation is not producing enough children to replace itself, eventually leading to an outright reduction in population.
Replacement level fertility is the level at which a population replaces itself from one generation to the next without migration. A decline in Total Fertility Rate (TFR) below the replacement level in many states of India would have a significant impact on the future population structure of the country.
Firstly, a decline in TFR would result in a decline in the population growth rate, which would lead to an aging population in the future. The proportion of older adults would increase, and the proportion of younger people would decrease. This would mean that there would be a higher dependency ratio, with fewer working-age people to support a growing population of older adults.
Secondly, a decline in TFR would also affect the population’s sex ratio, which is the number of males per 100 females in the population. India has a history of a skewed sex ratio, with a preference for male children leading to sex-selective abortions and female infanticide. However, a decline in TFR could lead to a more balanced sex ratio as families have fewer children and do not have a strong preference for male children.
Finally, a decline in TFR would have implications for the economy and the labor force. With fewer children being born, there would be a smaller pool of young people entering the workforce in the future. This could lead to labor shortages and a higher demand for automation and technology to compensate for the lack of available workers.
Overall, a decline in TFR below the replacement level in many states of India would have far-reaching implications for the country’s future population structure, including an aging population, a more balanced sex ratio, and potential labor shortages.
