QUES . Identify and discuss the factors responsible for diversity of natural vegetation in India. Assess the significance of wildlife sanctuaries in rain forest regions of India.UPSC 2023 GS MAINS PAPER I, 250 words, 15 Marks
भारत में प्राकृतिक वनस्पति की विविधता के लिए उत्तरदायी कारकों को पहचानिए और उनकी विवेचना कीजिए। भारत के वर्षा वन क्षेत्रों में वन्यजीव अभयारण्यों के महत्व का आकलन कीजिए।
HINTS:
India’s diverse natural vegetation is shaped by an interplay of diverse factors:
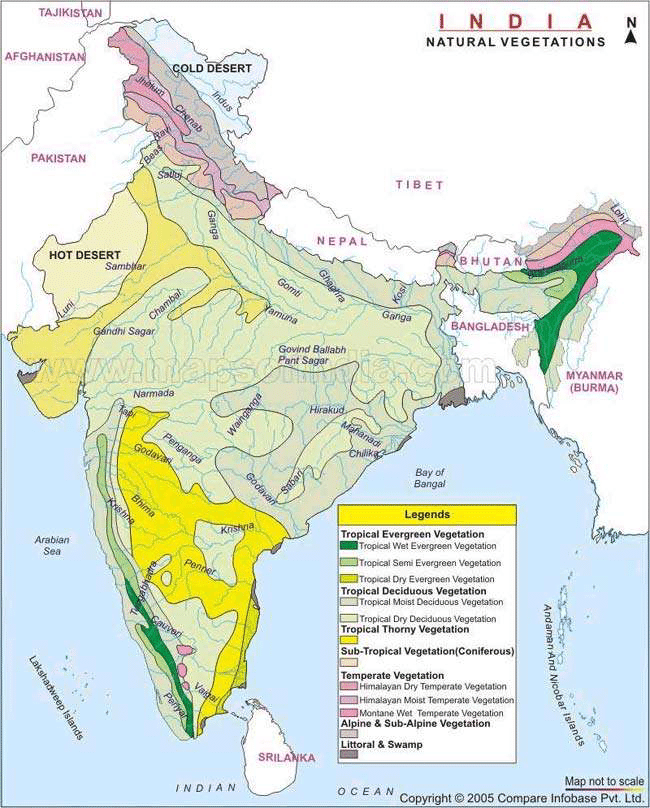
Factors responsible for diversity of natural vegetation in India:
The varied terrain and relief features of India, including mountains, plateaus, plains, and coastal areas, influence rainfall distribution and temperature gradients. This topographical diversity contributes to different vegetation types. For example lower altitude regions of Kerala have rain forests whereas high altitude regions have temperate sholas. Eastern Himalayas have dense forest as well as tree line upto higher altitude as compared to western Himalayas. Windward side of western ghats have tropical evergreen and leeward side has deciduous vegetation.
India’s vast subcontinental landmass spans a wide range of latitudes and longitudes.This subcontinental size exposes the country to various climatic influences resulting in diverse vegetation zones.
India’s location near the equator places a significant part of the country within tropical latitudes. This indicates high insolation, year-round higher temperatures as well as sufficient precipitation. Longer duration of sunlight promotes dense vegetation.
Temperature and precipitation are the major climatic factors that results in the formation of diverse agro-climatic regions and various types of natural vegetation. Areas of high rainfall and high temperature like western ghat region of Kerala, northeast region and Andaman and Nicobar Islands have evergreen forests. On the other hand western Rajasthan having high aridity has xerophytic vegetation.
India boasts a wide variety of soil types, including alluvial soils, red soils, black soils, and mountain soils. Soil characteristics influence the fertility and composition of vegetation in different regions. For example, edaphic factors like silt and clayey soil having good organic matter supports the growth of mangroves in the coastal regions as compared to sandy soils.
Significance of wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions of India:
Wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions serve as vital conservation areas for preserving India’s rich biodiversity. Biodiversity in the rainforest regions is very high therefore, wildlife sanctuaries in these regions provide a safe haven for endemic and endangered species, protecting them from poaching, habitat loss, and other threats.
Wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions regulate climate, control erosion, and maintain soil fertility.
Tropical rainforests in wildlife sanctuaries are also important because they sequester carbon dioxide, which is critical for world’s climate regulation, and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
Wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions support sustainable or eco-tourism, generating revenue and employment opportunities for local communities.
Wildlife sanctuaries aid in the preservation of the traditions and cultures of indigenous people residing in rainforests.
Thus, there is a wide range of vegetation types across the country whose conservation is important for preserving biodiversity and ecosystem services. Establishment of wildlife sanctuaries in rainforest regions is significant as it promotes this conservation.
